Erik Norland, CME Group
At a Glance:
- Typically, higher yield bonds have more correlation with equities, and investment grade bonds correlate with Treasuries
- Corporate bond futures allow investors to more precisely manage risk
1. Correlations
U.S. corporate bonds inhabit a space in the investment landscape that is somewhere in between U.S. Treasuries and equities. Investment grade bonds, like those in the Bloomberg U.S. Corporate Bond Index, usually correlate highly with U.S. Treasuries. However, that correlation can dip during periods of market stress like during the global financial crisis and the onset of the pandemic. During these scenarios, having a future specific to the needs of corporate bond investors could help them to mitigate risk.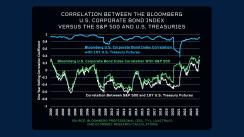
By contrast, high-yield bonds, such as those in the Bloomberg U.S. Corporate High Yield Very Liquid Index, usually correlate more strongly with the S&P 500 than with U.S. Treasuries.
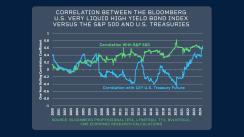
2. Scalability
Futures allow investors to scale risk exposures up and down. For example, risk parity strategies can use futures to scale U.S. Treasuries up to equity-like levels of risk. Up until now, scaling the risk of corporate bonds up to equity-like risk has been difficult, and both Bloomberg indices have rather low historical volatilities compared to equities.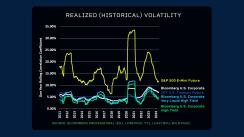
3. Optionality
Owning shares in a corporation is akin to owning call options on the value of a firm with a strike price of zero and no certain expiry. Unlike U.S. Treasuries, corporate bonds are not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. Instead, they depend on corporate cash flows to make good on their coupon and principal payments.As such, corporate bonds are akin to being long a U.S. Treasury plus a short put option on the value of a corporation. Their common dependence on the financial health of corporations are what gives corporate bonds, and especially high yield corporate bonds, their higher correlation with equities and their imperfect correlation with U.S. Treasuries.






